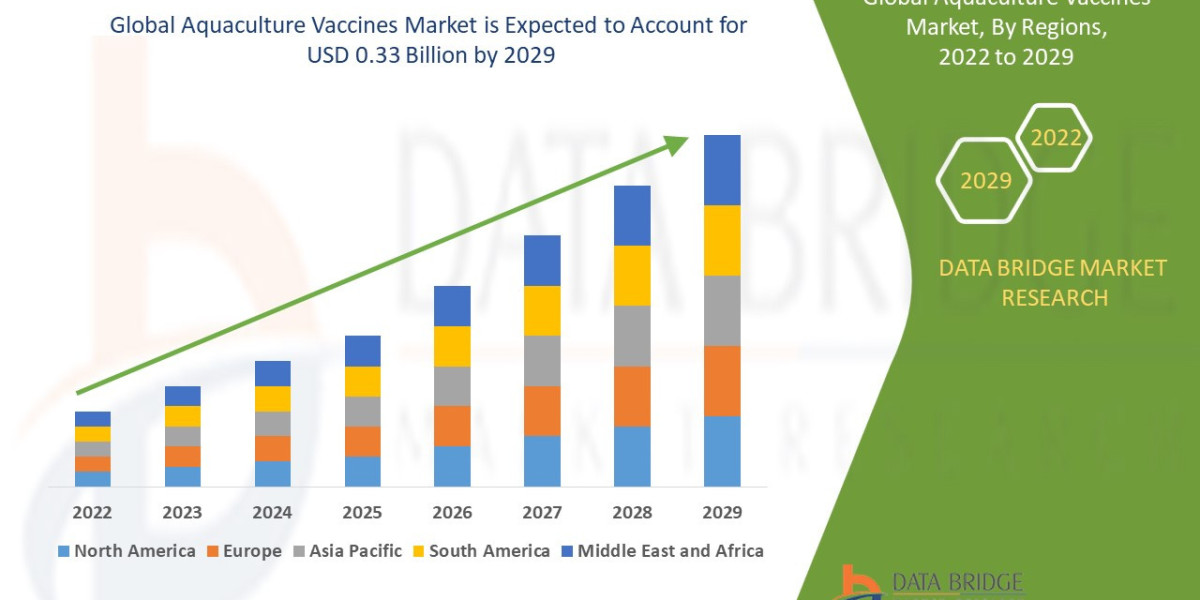
In today’s fast-growing power transmission and distribution networks, selecting the right overhead conductor is critical for long-term system reliability, safety, and lifecycle cost control. ACSR Cable (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced) remains one of the most trusted conductor technologies for overhead lines worldwide especially for utilities and EPC contractors working on long spans, heavy mechanical loading, and high-voltage transmission corridors.
As a global manufacturer of overhead conductors and power cables, HNBF Power supplies utility-grade ACSR cable solutions designed to meet international standards and the real-world demands of modern grid infrastructure.
This guide provides a clear, engineering-focused overview of ACSR cable, its construction, performance advantages, applications, and selection considerations for professional buyers.
What Is ACSR Cable?
ACSR Cable stands for Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced. It is a stranded overhead conductor consisting of:
One or more layers of hard-drawn aluminum wires
A central high-strength steel core
The aluminum strands carry the electrical current, while the steel core provides the mechanical strength required for long spans and high tension installations.
This dual-material structure allows ACSR cable to achieve an optimized balance between electrical conductivity and tensile performance, making it ideal for demanding overhead transmission environments.
Construction and Design of ACSR Cable
Aluminum Layers for Efficient Current Carrying
The outer aluminum strands in ACSR cable are responsible for:
High electrical conductivity
Low line losses compared to traditional copper conductors
Lightweight construction for easier handling during installation
Aluminum also offers excellent corrosion resistance in most atmospheric conditions.
Steel Core for Mechanical Strength
The steel core is engineered to:
Carry the majority of mechanical load
Control conductor sag under tension
Improve resistance to wind and ice loading
Depending on project requirements, the steel core may be galvanized or aluminum-clad for improved corrosion protection.
Key Performance Advantages of ACSR Cable
High Tensile Strength for Long Spans
One of the primary reasons utilities specify ACSR cable is its high strength-to-weight ratio. The reinforced steel core allows engineers to design longer spans between towers and reduce the number of supporting structures.
This directly contributes to:
Lower tower construction cost
Reduced foundation and right-of-way expenses
Simplified line routing in difficult terrain
Stable Sag Behavior under Load
ACSR cable maintains predictable sag characteristics even under heavy loading conditions such as:
High wind pressure
Ice accumulation
Elevated mechanical tension
This makes it suitable for overhead lines in harsh climates and wide river crossings.
Proven Reliability for Transmission Networks
ACSR cable has been used in transmission and sub-transmission networks for decades. Its long operational history makes it a preferred choice for utilities seeking proven conductor technology with well-established installation practices.
Typical Applications of ACSR Cable
ACSR cable is widely used across power networks, including:
High-voltage transmission lines
Medium-voltage overhead distribution lines
Long-distance interconnection projects
Mountainous, desert, and coastal transmission routes
River and highway crossings requiring long span capability
For EPC contractors and grid developers, ACSR cable remains a practical solution for projects where mechanical performance is as important as electrical efficiency.
ACSR Cable vs AAAC and AAC Conductors
ACSR vs AAC
AAC conductors use only aluminum strands and are best suited for short spans and urban distribution networks. In contrast, ACSR cable offers significantly higher tensile strength, making it more suitable for transmission corridors and long spans.
ACSR vs AAAC
AAAC conductors provide better corrosion resistance and slightly lower weight, but their mechanical strength is lower than that of ACSR cable. For projects exposed to heavy mechanical loading, ACSR remains the safer and more economical choice.
How to Select the Right ACSR Cable for Your Project
Electrical Capacity Requirements
Engineers must evaluate the required current-carrying capacity, short-circuit performance, and operating temperature limits to determine the appropriate conductor size.
Mechanical Loading and Span Length
Span length, wind pressure, ice load, and tower geometry directly influence conductor selection. ACSR cable is often selected when:
High tension is required
Long spans must be achieved without excessive sag
Environmental and Corrosion Considerations
In coastal or industrial environments, selecting appropriate steel core protection is critical. Proper surface treatment improves service life and reduces long-term maintenance costs.
HNBF Power’s ACSR Cable Solutions
As a global manufacturer serving power utilities, EPC contractors, and grid infrastructure developers, HNBF Power supplies a complete range of ACSR cable products engineered for overhead transmission and distribution systems.
HNBF Power focuses on:
Consistent conductor geometry and stranding accuracy
International standard compliance for utility projects
Reliable mechanical and electrical performance for long-term operation
Flexible production to support project-specific technical requirements
Whether for new transmission corridors or network upgrades, HNBF Power supports customers with technical consultation, drawing approval, and customized conductor design to meet specific project parameters.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Correct installation is essential to achieve the designed service life of ACSR cable.
Key practices include:
Proper stringing tension control
Avoiding surface damage to aluminum strands
Correct sag-tension calculation before installation
Suitable hardware and fittings compatible with ACSR construction
Following standard utility installation procedures helps maintain conductor integrity and ensures predictable long-term performance.
FAQs About ACSR Cable
1. What does ACSR cable stand for?
ACSR cable stands for Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced, combining aluminum strands for conductivity and a steel core for mechanical strength.
2. Is ACSR cable suitable for high-voltage transmission lines?
Yes. ACSR cable is widely used in high-voltage and extra-high-voltage overhead transmission projects due to its high tensile strength and proven reliability.
3. How does ACSR cable perform in harsh weather conditions?
ACSR cable performs well under wind and ice loading because the steel core carries most of the mechanical stress, helping maintain stable sag and line clearance.
4. Can ACSR cable be customized for specific utility projects?
Yes. ACSR cable can be manufactured in different aluminum and steel strand configurations to meet project-specific electrical and mechanical requirements.
5. Why do utilities still prefer ACSR cable over newer conductor types?
Many utilities prefer ACSR cable because of its long service history, well-defined standards, predictable performance, and wide availability of compatible fittings and hardware.
Final Thoughts
ACSR cable continues to play a vital role in modern overhead transmission and distribution systems. Its unique combination of electrical efficiency, mechanical strength, and proven operational performance makes it a dependable choice for utilities and EPC contractors worldwide.
If you are planning a new transmission line or upgrading existing infrastructure, contact HNBF Power today to discuss your technical requirements and receive customized ACSR cable solutions engineered specifically for your power transmission and distribution projects.